CSM Systems Overview
 |
|
CSM - Submerged
Hex Connection
|
 |
|
|
Diameter 3.5 - 3.8 - 4.2 - 4.6 - 5.3
Height 8 - 10 - 12 - 14
|
|
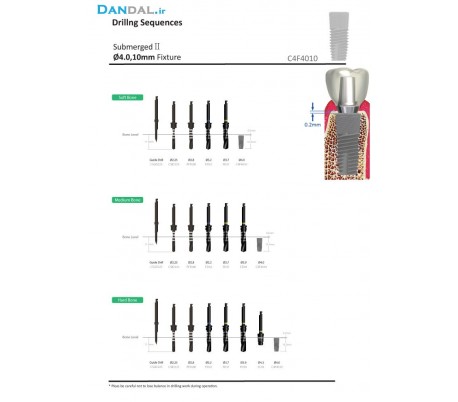
CSM - Submerged II
Double Hex Connection
|
 |
|
|
Diameter 3.5 - 4 - 4.5 - 5
Height 8 - 9 - 10 - 12 - 14
|
|
CSM - Submerged III
Double Hex (3.6) and Hex (4-4.8) Connection
|
 |
|
|
Diameter 3.6 - 4 - 4.4 - 4.8
Height 8 - 10 - 12 - 14
|
|
Internal Submerged
Octa Connection
|
 |
|
|
Diameter 3.5 - 4.1 - 4.8
Height 8 - 10 - 12 - 14
|
For more information Click on the above pictures.
- Ratchet with torque gauge
- Low price
- One driver for 3.8-5.3 sizes
- Various prosthetic components
- One drill for 8 / 10 and 12 / 14 mm lengths
- So many drill in surgical kit
- Separated driver for 3.5 mm fixtures
CSM Implant System
1- Submerged

- Hex Connection and Morse taper 11º ---> Prevention of bacterial penetrations and decrease bone loss
- Super micro thread (6 lines of micro threads) ---> Help quick placement, increase excellent initial stability and minimized bone less
- Dynamic body thread ---> Allows quick insertion and reduce the friction force
- Cutting edge ---> Self-tapping and primary stability
- RBM surface treatment ---> High osseointegration
- Laser surface treatment ---> Possibility of immediate loading
- Rounded apex ---> Reduced bone strength or sinus mandibular nerve
- Cylindrical shape
- Platform switching
2- Submerged II

- Double Hexagon Connection and Morse taper 11º ---> Prevention of bacterial penetrations and decrease bone loss
- Super micro thread (6 lines of micro threads) ---> Help quick placement, increase excellent initial stability and minimized bone less
- Dynamic body thread ---> Allows quick insertion and reduce the friction force
- RBM surface treatment ---> High osseointegration
- Cylindrical shape
- Cutting edge ---> Self-tapping and primary stability
- Platform switching
3- Internal

- Double Octagon Connection and Morse taper 8º ---> Prevention of bacterial penetrations and decrease bone loss
- Machined collar
- RBM surface treatment ---> High osseointegration
- Super micro thread (6 lines of micro threads) ---> Help quick placement, increase excellent initial stability and minimized bone less
- Cutting edge ---> Self-tapping and primary stability
- Rounded apex ---> Reduced bone strength or sinus mandibular nerve
- Cylindrical (Straight) and Tapered shape
- Dynamic body thread ---> Allows quick insertion and reduce the friction force
- Platform switching
4- The newest product of CSM is Submerged III
- Internal Hex for 3.6 diameter and double Hex connection for 4 to 4.8 diameters, this system is compatible with Submerged system.
- Active RBM surface
- Powerful Thread ---> Reduce stress and increase its stability
- Intensity cutting edge
Author: Review department of Dandal.ir
First Release Date: 2/Nov/2014
Last Modified: 15/May/2016
Sources:
- A removal torque of the laser-treated titanium implants in rabbit tibia. Biomaterials. 2003 Nov;24(26):4859-63
- Comparison of osseointegration between laser-etched and magnesium-incorporated oxidized implants in the rabbit femur. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants. 2013 May-Jun;28(3):77
- Comparison of Removal Torques for Laser-Treated Titanium Implants With Anodized Implants. J Craniofac Surg. 2011 Jul;22(4):1491-5
- Evaluation of a predictive model for implant surface topography effects on early osseointegration in the rat tibia model. J Prosthet Dent. 2001 Jan;85(1):40-6
- New Bone Formation Following Sinus Membrane Elevation Without Bone Grafting: Histologic Findings in Humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011 Jan;26(1):83-90
- Retrospective chart analysis on survival rate of fixtures installed at the tuberosity bone for cases with missing unilateral upper molars: a study of 7 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Jun;68(6):1338-44
- Retrospective multicenter study of CSM endosseous dental implant. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2007 Jun 45(3):321-328
- The bone integration effects of platelet-rich fibrin by removal torque of titanium screw in rabbit tibia. Platelets. 2014;25(8):562-6
- The effects of laser etching on shear bond strength at the titanium ceramic interface. J Prosthet Dent. 2009 Feb;101(2):101-6
- The effect of water pyrolysis on the removal torque of titanium implant inserted in rabbit tibias. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011 Feb;22(2):157-64
- The influence of systemically administered oxytocin on the implant-bone interface area: an experimental study in the rabbit. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014 Dec;6(6):505-11
- The relation between surface roughness and interfacial shear strength for bone-anchored implants. A mathematical model. J Biomech. 1999 Aug;32(8):829-36
- The removal torque of titanium screw inserted in rabbit tibia treated by dual acid etching. Biomaterials. 2003 Sep;24(20):3611-7